Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
NHS-Biotin: Enabling Next-Gen Protein Multimerization & I...
2025-09-26
Discover how NHS-Biotin, a leading amine-reactive biotinylation reagent, empowers advanced protein engineering strategies beyond traditional labeling—enabling multimerization, intracellular tracking, and novel purification workflows. This in-depth analysis uniquely integrates membrane-permeable biotinylation chemistry with cutting-edge multimeric protein research.
-
Trichostatin A (TSA): Epigenetic Precision in Cancer and ...
2025-09-25
Explore how Trichostatin A (TSA), a leading histone deacetylase inhibitor, empowers advanced epigenetic research through precise modulation of cell fate and cancer proliferation. This in-depth article reveals novel insights into TSA’s mechanism, organoid applications, and comparative advantages over alternative HDAC inhibitors.
-
Filipin III: Unraveling Cholesterol Microenvironments in ...
2025-09-24
Explore how Filipin III, a polyene macrolide antibiotic, enables unprecedented insight into cholesterol microenvironments, membrane dynamics, and disease mechanisms. This article uniquely connects cholesterol-binding fluorescent antibiotic technology with advanced cell biology and metabolic research.
-
ABT-263 (Navitoclax): Novel Insights into Pol II-Driven A...
2025-09-23
Explore how ABT-263 (Navitoclax), a potent Bcl-2 family inhibitor, advances caspase-dependent apoptosis research by intersecting mitochondrial and nuclear apoptotic signaling in cancer biology. This article synthesizes recent findings on RNA Pol II-mediated cell death, offering new directions for oral Bcl-2 inhibitors in cancer research.
-
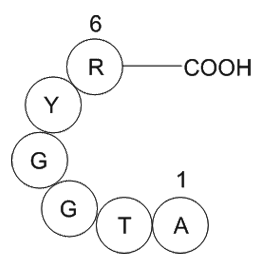
The GRAVY value for a protein is calculated as the
2025-04-19
The GRAVY value for a protein is calculated as the sum of hydropathy values of all the amino acids, divided by the number of residues in the sequence (Kyte and Doolittle, 1982). According to Kyte and Doolittle (1982) integral membrane proteins typically have higher GRAVY scores than do globular prot
-
br Disclaimer Statement br Acknowledgments br Introduction
2025-04-18
Disclaimer Statement Acknowledgments Introduction Metabolic changes are a common feature of cancerous tissues. Mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes cause alterations to multiple intracellular signaling pathways that rewire tumor cell metabolism and re-engineer it to allow enhan
-
It has also been reported
2025-04-17
It has also been reported that defects in ATM or ATR signalling are synthetically lethal with PARP inhibition (Turner et al., 2008, Peasland et al., 2011, Yap et al., 2011, Michels et al., 2014), suggesting that combined inhibition of PARP and ATM or ATR may be an effective therapeutic strategy. In
-
ASK belongs to the family of MAPKKK
2025-04-15
ASK1 belongs to the family of MAPKKK. ASK1-mediated apoptosis is involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases such as I/R injury, infectious diseases and neurodegenerative disorders [33], [34], [35]. ASK1 can be activated through different mechanisms. One mechanism is that oxidative stress direc
-
Although the exact mechanisms are not fully understood IGF i
2025-04-14
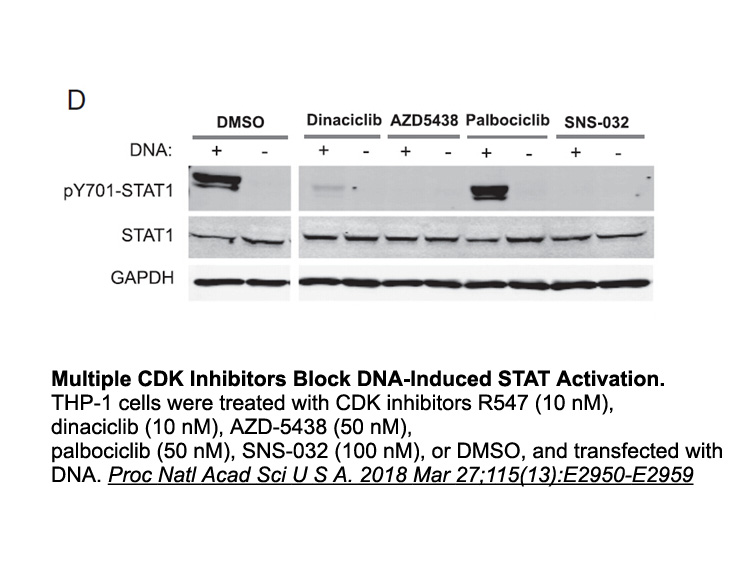
Although the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, IGF-1 is tightly linked with ER and estrogen actions and a crosstalk occurs between these two systems in breast cancer. To illustrate this close relationship, studies have identified a synergy between IGF-1 and estrogen in Sulfo-NHS-Biotin exp
-
The MOB and AOB are important in
2025-04-12
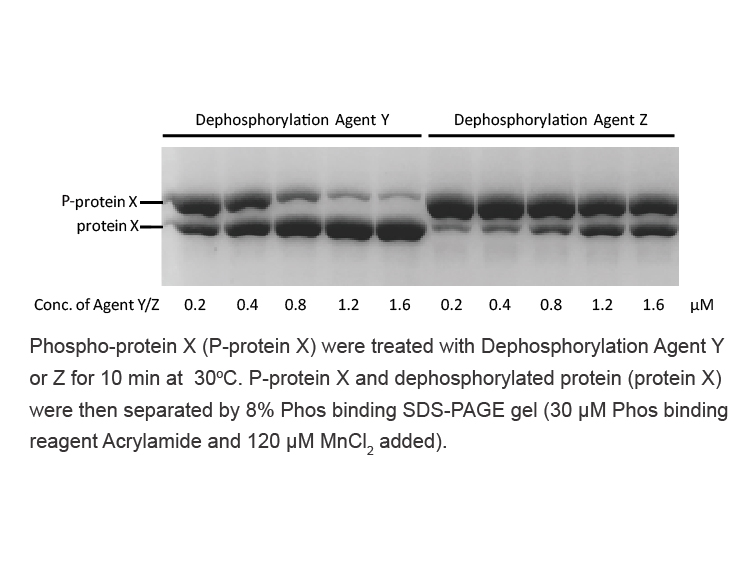
The MOB and AOB are important in ungulates (Keller and Levy, 2012, Sanchez-Andrade and Kendrick, 2009), which rely heavily on odorant information for social interactions (Baum and Cherry, 2015, Keller and Levy, 2012, Osada et al., 2014, Villagran and Ungerfeld, 2013). The release of GABA and glutama
-
Sulfo-NHS-Biotin It is reported that calpain plays a
2025-04-11
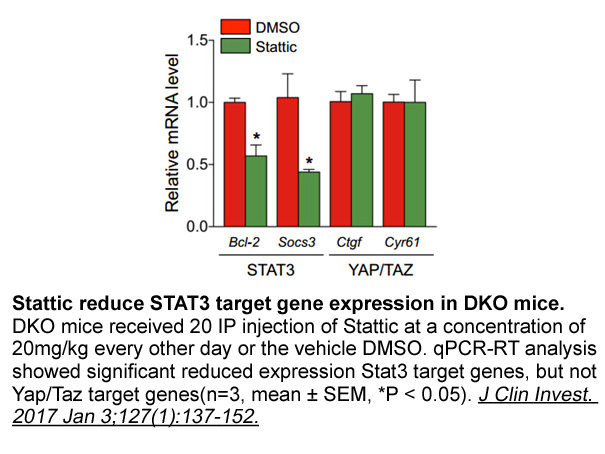
It is reported that calpain-2 plays a critical role in BDNF-induced signaling and memory formation, and knockdown of calpain-2, but not calpain-1, completely suppresses BDNF-induced pathway activation and protein translation (Briz et al., 2013). BDNF prevents neuronal apoptosis or death (Ferrer et a
-
br Secreted enzymes Only two
2025-04-11

Secreted enzymes Only two secreted S. aureus enzymes reportedly induce apoptosis, namely, staphylococcal staphopain B (SspB) and coagulase. SspB selectively cleaved CD11b/CD18 integrin and induced an apoptosis-like cell death in neutrophils and monocytes (Smagur et al., 2009). Neutrophils or mono
-
In summary these data show that agonist exposure induces int
2025-04-10
In summary, these data show that agonist exposure induces internalization and reduction in cell surface HA-mAPJ expression that occurs relatively rapidly during agonist exposure and recovers more slowly after agonist removal. Moreover the ppERK response of mAPJ-HEK293 cells to [Pyr1]apelin-13 desens
-
Besides one should also consider that all antioxidant compou
2025-04-09
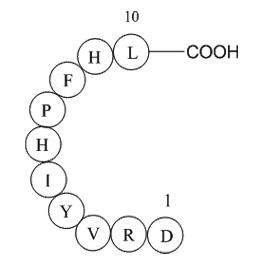
Besides, one should also consider that all antioxidant compounds (free soluble or insoluble bounds) exist all together in colon, where radicals and antioxidant compounds react continuously with each other. At this point, after the consumption of antioxidants bound to dietary fiber, they reach the co
-
br Introduction Humans have consumed mushrooms for centuries
2025-04-09
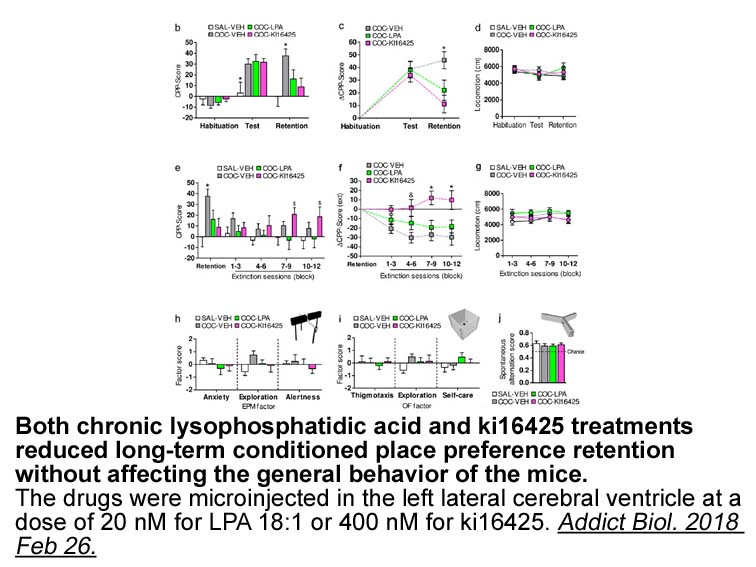
Introduction Humans have consumed mushrooms for centuries because of their high nutrient content and low lipid content, as well as their excellent flavor and texture [1]. Edible mushrooms possess notable medicinal properties and bioactivities, including antitumor, antiviral, antidiabetic, and ant
16047 records 13/1070 page Previous Next First page 上5页 1112131415 下5页 Last page